A new Architechture for Talkie: TalkiePCM
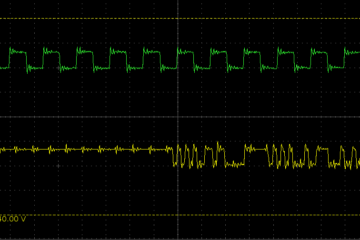
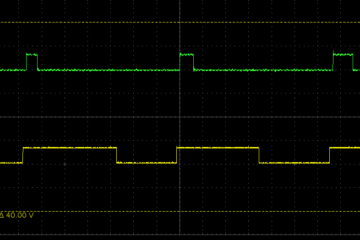
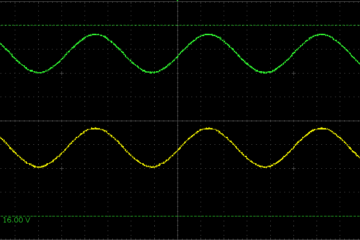
There are quite a few popular TTS libraries for Arduino but most of them suffer from the same problem: The TTS function is not properly separated from the output function. Architechture In a properly architected solution we would have a A TTS function which produces platfrom independent PCM data An output function or library to process the PCM data. In Arduino we have the abstact Print class which is used by everything to which you Read more