The easiest way to “record” audio with an Arduino UNO R4 is by using an analog microphone which can be connected to any analog pin.
For my test I was using a MCP6022 Microphone Sensor.

Arduino Sketch
There are no surprises here because we can use the AnalogAudioStream as audio source:
#include "AudioTools.h"
AnalogAudioStream in;
AudioInfo info(8000, 1, 16);
CsvOutput<int16_t> out(Serial); // ASCII output stream
StreamCopy copier(out, in); // copy i2sStream to CsvOutput
// Arduino Setup
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
AudioLogger::instance().begin(Serial, AudioLogger::Info);
// RX automatically uses port 0 with pins GPIO34,GPIO35
auto cfgRx = in.defaultConfig(RX_MODE);
//cfgRx.start_pin = A1; // define pin - default is A0
//cfgRx.is_auto_center_read = true; // default is true
cfgRx.copyFrom(info);
in.begin(cfgRx);
// open output
out.begin(info);
}
// Arduino loop - copy data
void loop() {
copier.copy();
}
The potentially upated source code for this “streams-adc-serial” example can be found in the Project and on Github
Pin Mapping
MIC – UNO
VCC – 5V
GND – GND
OUT – A0
When no pin is defined in the configuration, we automatically use A0.
Result
I suggest to record a sine wave that was generated e.g. with the help of https://onlinetonegenerator.com
Here is the result displayed with the help of the Arduino Serial Plotter:
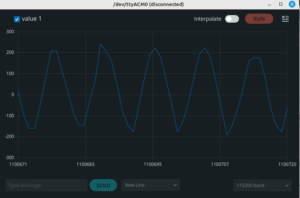
We can see that this resembles a sine wave that is centered around 0, but the quality is not perfect. However this is still good enough for further processing: We can e.g. use this as input into FFT to analyse the frequency spectrum and display the result on the LED matrix…


0 Comments